The Future Is Now: A Look At The Latest 3d Printing Technologies
3D printing can be a very exciting technology, and the field is constantly evolving. But it's also easy to feel overwhelmed by all the latest developments—and to think that you'll never see them in action. In this blog post, we'll explore some of the most exciting new developments in 3D Printing technologies and materials, including new ways to use them at home or in school.
3D Printing Technologies
It's hard to believe that 3D printing was invented in the 1980s. Since then, it has grown into a multi-billion dollar industry with many different technologies and applications.
Here are the most common types of 3D printing:
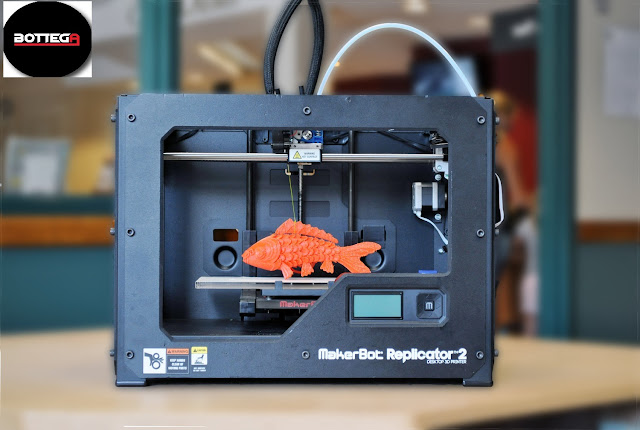
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common type of desktop 3D printer that uses melted plastic filament as its building material. It works by laying down lines or layers of molten plastic that cool after being deposited onto an object; this results in a solidified structure with no support material required during fabrication (the exception being when using certain types of filaments).
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses computer-controlled lasers to fuse powdered materials together into complex geometries without needing any sort of support structure during fabrication (for example: metal powders). This allows for more complex shapes than those possible with other technologies due to its ability to create solid parts directly from powder without first creating their mold form beforehand like other processes do; however they tend not be as strong as those created through other methods because they lack internal reinforcement due to having been built up layer-by-layer rather than by melting/vaporizing entire blocks like traditional liquid casting techniques do which means they're usually only used for prototypes instead.
3D Printing Materials
There are a number of materials you can use with your 3D printer, depending on what you're trying to achieve. Here are the most common:
- PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable thermoplastic that's made from renewable resources like corn or sugarcane. It's ideal for printing prototypes and figurines because it doesn't warp or crack when exposed to heat and humidity.
- ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is another thermoplastic material that's used in many household products such as toys and electronics enclosures--but beware: ABS tends to warp when printed in large parts at high temperatures!
- PVA (polyvinyl acetate) is similar to PLA but has more flexibility; this makes it suitable for printing objects like shoes or bags where flexibility is important
3D Printing Service Providers
3D printing service providers are a new and emerging industry. They allow you to get your idea made into reality without having to learn how to use the technology yourself, or even own the equipment required for 3D printing.
3D Printing Service providers can help you with all stages of your project, from concept design through production and delivery.
Some 3D printing service providers will only handle small-scale projects, while others have the facilities to take on large-scale projects.
3D printing service providers can help you with all stages of your project, from concept design through production and delivery. Some 3D printing service providers will only handle small-scale projects, while others have the facilities to take on large-scale projects.
Conclusion
3D printing is an exciting technology, and the future looks even brighter. We are excited to see what new innovations come next!


Comments
Post a Comment